If you’ve ever noticed a pipe sticking out of your roof and wondered, “How far above a roof must a plumbing vent extend?”—you’re not alone. This seemingly small detail plays a critical role in your home’s plumbing system, preventing sewer gases from entering your living space and ensuring proper drainage. Getting the height wrong can lead to health hazards, code violations, or even system failure. Let’s break down exactly what the codes say—and why it matters.
Why Does Plumbing Vent Height Matter?
Plumbing vents aren’t just random pipes—they’re essential for balancing air pressure in your drainage system. Without proper venting, water can’t flow smoothly through pipes, leading to gurgling drains, slow flushing toilets, or even sewer gas backup.
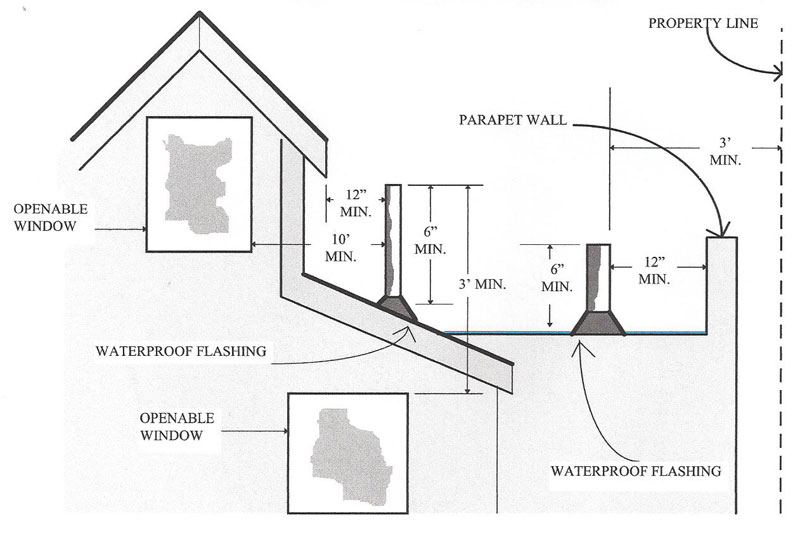
More importantly, if a vent terminates too close to windows, doors, or air intakes, toxic gases like methane and hydrogen sulfide can seep back into your home. That’s why building codes strictly regulate how high these vents must rise above the roof surface.
What Do Building Codes Say About Vent Height?
In the United States, the International Plumbing Code (IPC) is the primary standard adopted by most states and municipalities. According to IPC Section 905.1, a plumbing vent must extend:
“Not less than 6 inches (152 mm) above the roof surface.”
But that’s not the whole story.
Additional Requirements Based on Roof Type & Use
| Roof Type | Minimum Vent Extension | Special Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Standard sloped roof | 6 inches | Measured vertically from roof surface |
| Roof used for sunbathing or assembly | 7 feet (2134 mm) | To prevent human exposure to gases |
| Near vertical walls or parapets | 6 inches above highest point within 10 ft | Prevents downdrafts trapping gases |
| In snowy climates | Often extended higher | Prevents blockage from snow buildup |
💡 Pro Tip: Local amendments may apply. Always check with your city or county building department, as some areas (like Chicago or parts of California) have stricter rules.
For more on plumbing systems and their design principles, see the Wikipedia entry on plumbing.
Common Mistakes Homeowners Make
Even well-intentioned DIYers often get vent height wrong. Here are frequent errors:
- Measuring horizontally instead of vertically: The 6-inch rule is vertical clearance, not diagonal.
- Ignoring roof slope: On steep roofs, the vent must still clear 6″ at the point where it penetrates the roof—not at the ridge.
- Placing vents too close to openings: Vents must be at least 10 feet horizontally from any window, door, or air intake—or extend 7 feet above those openings.
- Using improper materials: PVC is standard, but metal may be required in high-wind or fire-prone zones.
These mistakes might seem minor, but they can cause failed inspections, costly rework, or worse—health risks.
Step-by-Step: Installing a Code-Compliant Plumbing Vent
Follow these steps to ensure your vent meets all requirements:
- Determine roof penetration point
Choose a location at least 10 feet from any operable window or fresh-air intake. - Cut the roof opening
Use a reciprocating saw to create a clean hole for the vent pipe (typically 2″ or 3″ diameter). - Install flashing
Slide roof flashing under shingles to prevent leaks. Seal edges with roofing cement. - Extend the vent pipe
- For standard roofs: minimum 6 inches above the roof surface, measured vertically.
- For occupied roofs (e.g., rooftop decks): minimum 7 feet above the walking surface.
- Secure and cap (if needed)
Use pipe straps to anchor the vent. Install a bird guard or rain cap—but never a sealed cap, which blocks airflow. - Inspect locally
Call your local building inspector before closing walls or finishing the roof.
✅ Real-World Example: In Denver, CO, a homeowner installed a vent only 4″ above the roof. During winter, snow covered it completely, causing a backup of sewer gas into the bathroom. A $200 fix became a $2,500 remediation job after drywall removal and air quality testing.
How Climate Affects Vent Height Requirements
While the IPC sets a national baseline, climate plays a big role in practical installation:
- Snowy regions (e.g., Minnesota, Vermont): Builders often extend vents 12–24 inches to avoid snow blockage.
- High-wind coastal areas (e.g., Florida, Carolinas): Vents may need reinforced brackets and taller extensions to prevent downdrafts.
- Urban settings with flat roofs: Rooftop HVAC units or penthouses may require vents to rise above adjacent structures.
According to a 2023 study by the National Association of Home Builders (NAHB), 28% of plumbing-related callbacks in cold climates were due to improperly extended vents.
Plumbing Vent Height: FAQs
Q1: Can a plumbing vent be horizontal?
A: Only in limited cases. Vents must rise vertically until they’re at least 6 inches above the roof or the highest flood level of connected fixtures. Horizontal runs are allowed inside the building but must maintain proper slope and avoid traps.
Q2: Do I need a vent for every drain?
A: Not necessarily. Multiple fixtures can share a common vent stack, but each trap must be vented within a specific distance (usually 5 feet for a 2″ pipe). This is called “wet venting” and is governed by IPC Table 906.1.
Q3: What happens if my vent is too short?
A: Short vents can allow sewer gases to enter the home, cause slow drainage, or lead to trap siphoning—where water is sucked out of P-traps, breaking the seal against odors.
Q4: Can I extend my existing vent myself?
A: Yes—if you’re comfortable working on a roof and understand local codes. But if you’re unsure, hire a licensed plumber. A mistake could violate insurance or resale requirements.
Q5: Are there alternatives to roof vents?
A: Yes. Air admittance valves (AAVs), like Studor vents, can be used in some jurisdictions as a one-way mechanical vent. However, many inspectors still prefer traditional roof vents for reliability. Check local approval before installing.
Q6: Does the vent pipe diameter matter?
A: Absolutely. Most residential vents are 2 inches in diameter. Reducing size can restrict airflow and defeat the purpose of venting. Never use a pipe smaller than the drain it serves.
Conclusion
Knowing how far above a roof a plumbing vent must extend isn’t just about passing an inspection—it’s about protecting your family’s health, ensuring your plumbing works efficiently, and avoiding costly repairs. Stick to the 6-inch minimum (or 7 feet for occupied roofs), account for local climate and building use, and when in doubt, consult a professional.
✅ Your next step: Share this guide with a friend who’s renovating—or save it for your next home project! Got questions? Drop them in the comments below.
Stay safe, stay vented, and keep those drains flowing smoothly!
📌 Like this post? Share it on Facebook, Pinterest, or Twitter to help others avoid plumbing pitfalls!
Leave a Reply