If you’ve ever noticed a foul odor wafting from your drains or heard gurgling sounds after flushing the toilet, your plumbing vent might be the culprit. One of the most frequently asked questions homeowners and DIYers have is: how high does a plumbing vent need to be? Getting this wrong can lead to poor drainage, sewer gas leaks, or even failed inspections. In this guide, we’ll break down the exact height requirements, explain the why behind the rules, and help you stay compliant with U.S. plumbing codes—so your system works safely and efficiently.
What Is a Plumbing Vent and Why Does Height Matter?
A plumbing vent is a pipe that extends from your drainage system through your roof. Its job is twofold:
- Allow sewer gases to escape safely outdoors
- Maintain proper air pressure in the drainage system so water flows smoothly without siphoning trap seals.
If the vent is too short, wind or snow can force sewer gases back into your home. If it’s too close to windows or air intakes, those same gases can re-enter your living space. That’s why height and placement aren’t just suggestions—they’re code-enforced safety measures.
According to the International Plumbing Code (IPC)—the standard adopted by most U.S. states—the minimum height is clearly defined.
What Is the Minimum Height for a Plumbing Vent Pipe?
Per the 2021 International Plumbing Code (IPC) Section 904.1, a plumbing vent must extend at least 6 inches (152 mm) above the roof surface. However, that’s just the baseline. Additional rules apply based on proximity to other structures:
| Standard roof penetration | ≥ 6 inches above roof |
| Within 10 feet of a window, door, or air intake | ≥ 2 feet (24 inches) above the opening |
| On a flat or low-slope roof used for occupancy (e.g., rooftop deck) | ≥ 7 feet (84 inches) above the walking surface |
💡 Pro Tip: Local building codes may be stricter. Always check with your city or county before finalizing your installation.
These rules exist because sewer gases like hydrogen sulfide and methane are not only smelly—they’re hazardous in high concentrations. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) notes that even low-level exposure can cause headaches or nausea.
How Close Can a Vent Be to a Window or HVAC Unit?
This is a common oversight. Many homeowners install vents just above the roofline but forget about nearby windows or mechanical air intakes.
IPC Section 904.3 states:
“Vents extending through the roof shall be extended not less than 2 feet (610 mm) above the highest adjacent roof surface within 10 feet (3048 mm).”
In plain English: if your vent pipe is within 10 feet of a window, skylight, or HVAC intake, it must rise at least 2 feet higher than that opening. This prevents wind from blowing sewer gases back inside.
For example:
- Your bathroom window is 4 feet above the roof.
- Your vent is 8 feet away from that window.
- → Your vent must be at least 6 feet above the roof (4 ft + 2 ft = 6 ft).
Failure to comply often leads to failed inspections or chronic odor issues.
Do All Vents Need to Go Through the Roof?
Not always—but most do. While the IPC allows alternative venting methods (like air admittance valves or island vents), roof vents remain the gold standard for whole-house systems.
Air Admittance Valves (AAVs) are one exception. These mechanical devices allow air into the system but prevent sewer gases from escaping. They’re useful under sinks or in island countertops where roof venting isn’t practical. However:
- AAVs cannot replace the main roof vent.
- They require proper installation and periodic maintenance.
- Not all jurisdictions allow them (e.g., some parts of California restrict their use).
For full reliability and code compliance, a roof-penetrating vent is still recommended for the primary drainage stack.
📚 Learn more about venting systems on Wikipedia’s plumbing vent page .
Step-by-Step: Installing a Code-Compliant Roof Vent
Follow these steps to ensure your vent meets height and safety standards:
- Locate the main drain stack – Usually a 3- or 4-inch vertical pipe running from your basement to the roof.
- Extend the pipe through the roof – Use the same diameter pipe (typically PVC or cast iron).
- Cut the roof carefully – Avoid rafters; use a roofing boot to seal the penetration.
- Measure height from the roof surface – Use a tape measure from the highest point of the roof within 10 feet.
- Trim or extend the pipe so it meets the minimum height:
- 6 inches above roof (standard)
- 24+ inches if near windows/air intakes
- 84 inches if on a walkable roof
- Secure and seal – Use roofing cement and a proper flashing boot to prevent leaks.
- Inspect – Have a licensed plumber or building inspector verify compliance.
⚠️ Warning: Never cap or block a vent pipe. Doing so can cause slow drains, gurgling toilets, or dry P-traps—leading to dangerous gas infiltration.
Common Mistakes Homeowners Make with Vent Height
Even experienced DIYers slip up. Here are the top errors—and how to avoid them:
- Mistake #1: Installing the vent flush with the roof shingles.
→ Fix: Always extend at least 6 inches above. - Mistake #2: Ignoring nearby windows or decks.
→ Fix: Measure 10 feet in all directions; raise vent if needed. - Mistake #3: Using undersized pipe.
→ Fix: Vent diameter should match or exceed the drain stack (usually 3–4 inches). - Mistake #4: Sealing the vent with mesh or caps to keep out debris.
→ Fix: Vents must remain open to atmosphere. Use a bird guard if necessary, but never a solid cap.
FAQ: Plumbing Vent Height Questions Answered
Q1: Can a plumbing vent be horizontal?
Yes—but only for short runs. The IPC allows horizontal vent sections, but they must slope upward at least 1/4 inch per foot toward the vertical stack to prevent water trapping.
Q2: What happens if my vent is too short?
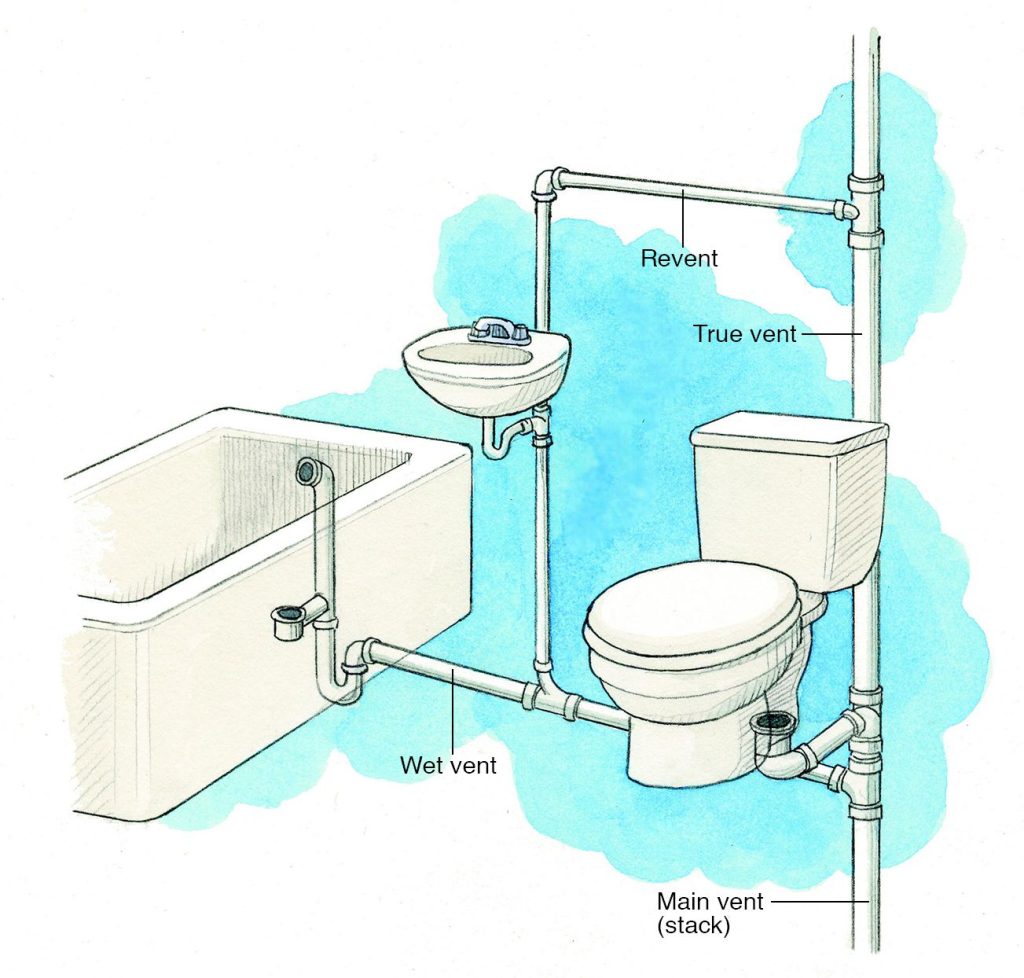
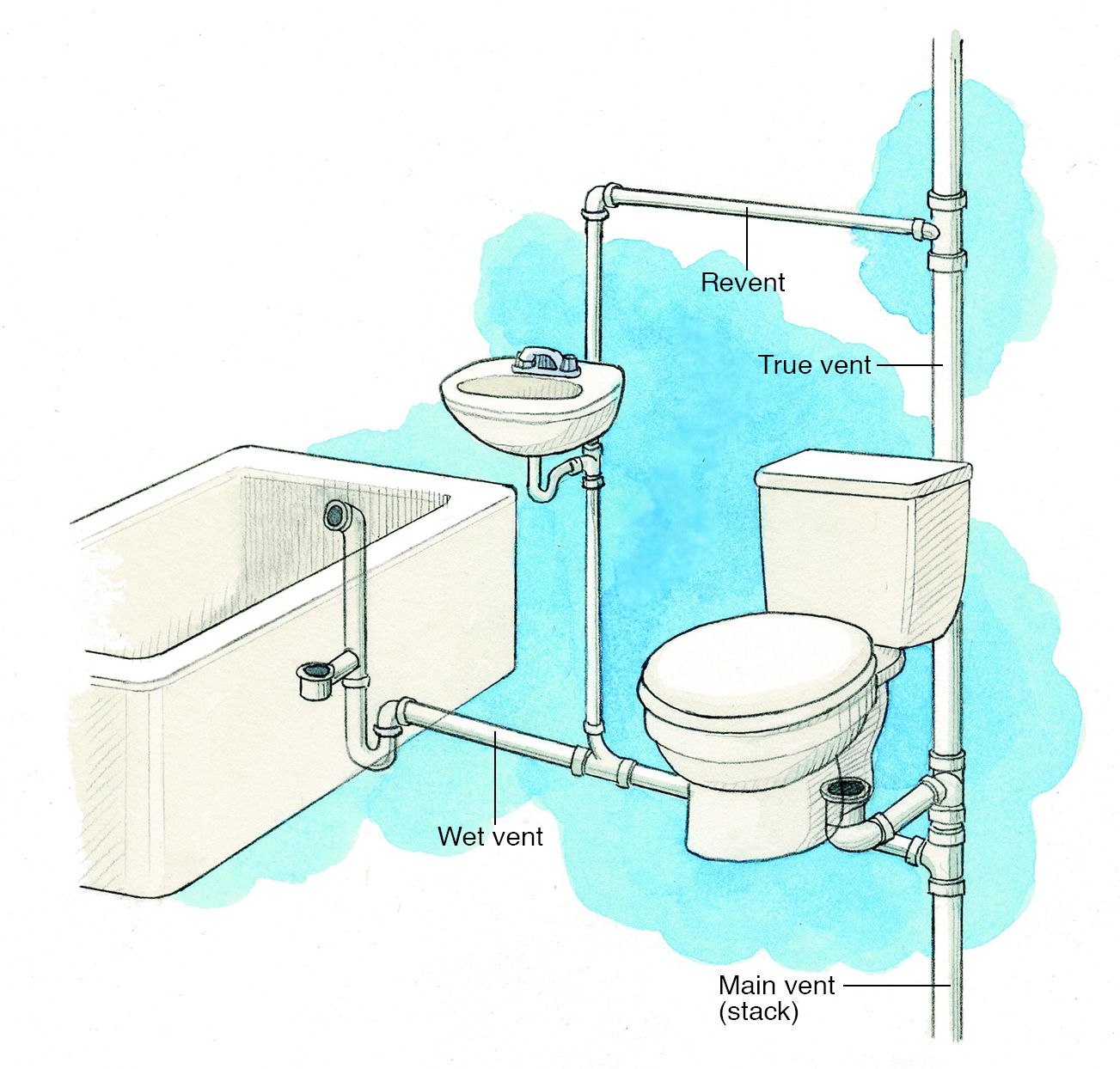
A short vent can allow sewer gases to enter your home, cause slow drainage, or lead to siphoned P-traps (which lose their water seal). You might notice foul odors or gurgling sounds.
Q3: Do plumbing vents need to be insulated?
In cold climates, yes. If the vent runs through unheated spaces, insulate it to prevent frost buildup that can block airflow. Blocked vents in winter are a leading cause of indoor sewer smells.
Q4: How far can a vent be from a toilet?
Per IPC, a toilet’s vent must connect within 6 feet of the trap. Beyond that, you risk siphoning and poor flushing performance.
Q5: Can I share a vent between multiple fixtures?
Yes—this is called a wet vent. But sizing and layout must follow code. For example, a 2-inch vent can typically serve a bathroom group (toilet, sink, shower) if properly configured.
Q6: Who should I call if I suspect a venting issue?
Contact a licensed plumber. They can perform a smoke test or pressure test to diagnose vent problems safely and accurately.
Conclusion
Knowing how high a plumbing vent needs to be isn’t just about passing an inspection—it’s about protecting your home, health, and comfort. Whether you’re building new, remodeling, or troubleshooting odors, following IPC guidelines ensures your system works as designed.
Remember:
- Minimum 6 inches above roof
- 2 feet above nearby openings
- Never cap or block the vent
Got a smelly drain or gurgling toilet? This simple fix might be all you need. If this guide helped you, share it with a friend or on social media—they might be dealing with the same hidden plumbing issue!
Stay safe, stay ventilated, and keep those drains flowing smoothly.
Leave a Reply